6. Advanced Routing Queries¶
Routing, is not limited to pedestrians and most of the time is used for routing vehicles.
Chapter Contents
6.1. Routing for Vehicles¶
A query for vehicle routing generally differs from routing for pedestrians:
The road segments are considered directed,
Costs can be:
Distance
Time
Euros
Pesos
Dollars
CO2 emissions
Wear and tear on the vehicle, etc.
The
reverse_costattribute must be taken into account on two way streets.The costs should have the same units as the
costattributecostandreverse_costvalues can be different
Due to the fact that there are roads that are one way:
Depending on the geometry, the valid way:
(
source, target) segmentIF cost >= 0 AND reverse_cost < 0(
target, source) segmentIF cost < 0 AND reverse_cost >= 0
A wrong way is indicated with a negative value and is not inserted in the graph for processing.
Two way roads - IF cost >= 0 AND reverse_cost >= 0 and their values can
be different. For example, it is faster going down hill on a sloped road.
In general, cost and reverse_cost do not need to be length; they can be
almost anything, for example time, slope, surface, road type, etc., or they can
be a combination of multiple parameters.
The following queries indicate the number of road segments, where a “one way” rule applies:
Number of (source, target) segments with
cost < 0SELECT count(*) FROM ways WHERE cost < 0;
count ------- 0 (1 row)
Number of (target, source) segments with
reverse_cost < 0SELECT count(*) FROM ways WHERE reverse_cost < 0;
count ------- 6388 (1 row)
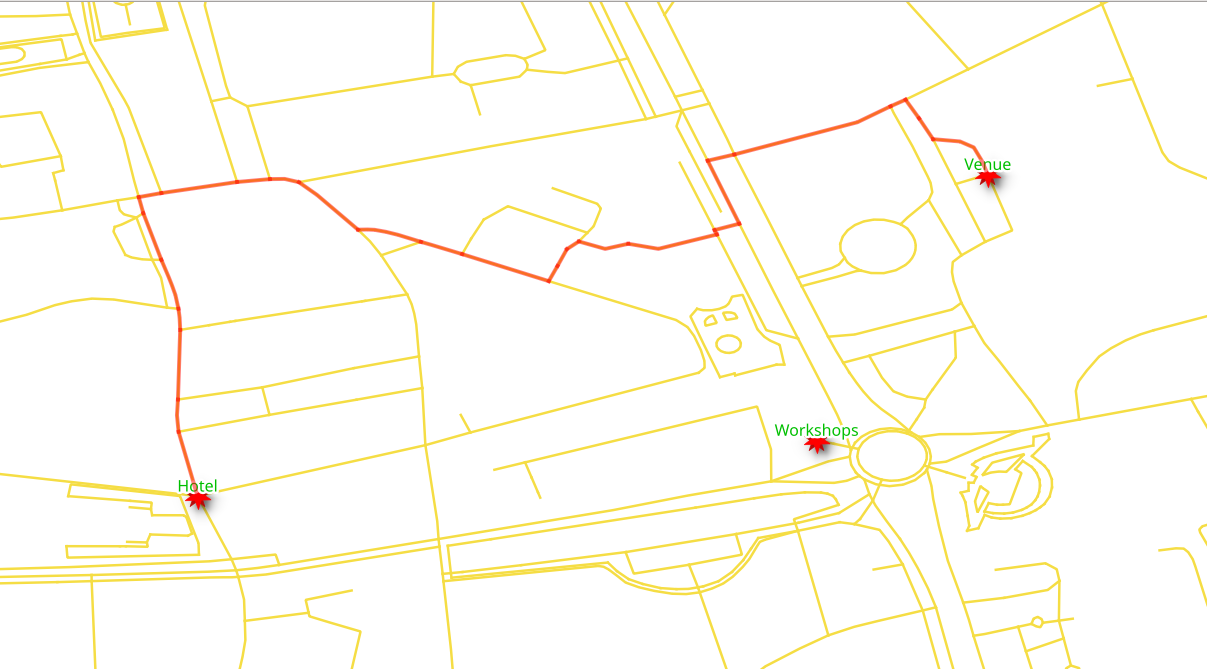
6.1.1. Exercise 7 - Vehicle routing - Going¶
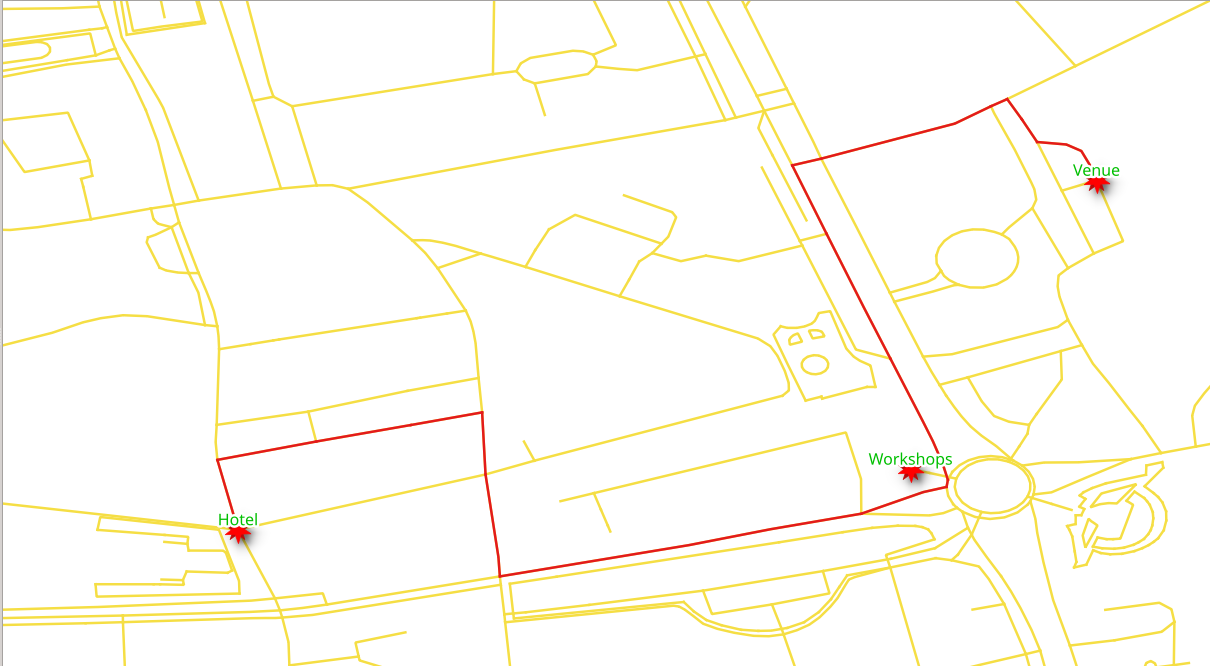
From the venue at National Theater Bucharest to the Hotel Capitol by car.

The vehicle is going from vertex
16826to279.Use
costandreverse_costcolumns, which are in unitdegrees.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 | SELECT * FROM pgr_dijkstra(
'
SELECT gid AS id,
source,
target,
cost_s AS cost,
reverse_cost_s AS reverse_cost
FROM ways
',
16826,
279,
directed := true);
|
6.1.2. Exercise 8 - Vehicle routing - Returning¶
From Hotel Capitol to the venue at National Theater Bucharest by car.
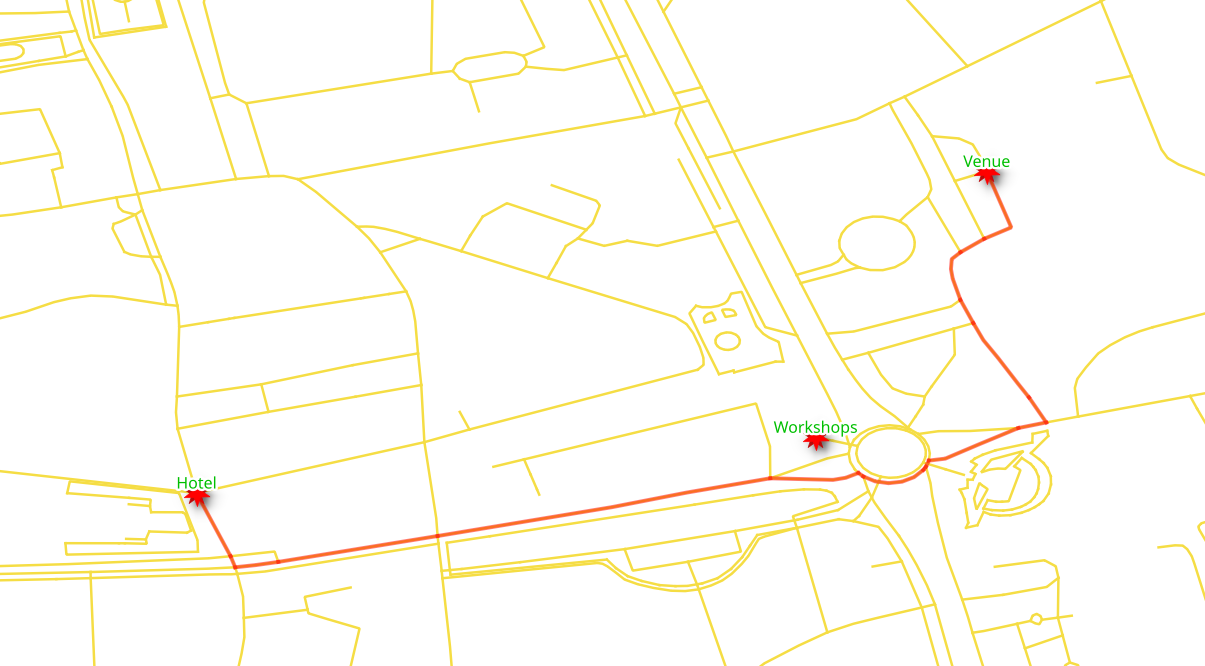
The vehicle is going from vertex
279to16826Use
costandreverse_costcolumns, which are in unitdegrees.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 | SELECT * FROM pgr_dijkstra(
'
SELECT gid AS id,
source,
target,
cost_s AS cost,
reverse_cost_s AS reverse_cost
FROM ways
',
279,
16826,
directed := true);
|
Note
On a directed graph, going and coming back routes, most of the time are different.
6.1.3. Exercise 9 - Vehicle routing when “time is money”¶
From Hotel Capitol to the venue at National Theater Bucharest by taxi.

The vehicle is going from vertex
279to16826The cost is
$100 per hour.Use
cost_sandreverse_cost_scolumns, which are in unitseconds.The duration in hours is
cost / 3600The cost in
$iscost / 3600 * 100
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 | SELECT * FROM pgr_dijkstra(
'
SELECT gid AS id,
source,
target,
cost_s / 3600 * 100 AS cost,
reverse_cost_s / 3600 * 100 AS reverse_cost
FROM ways
',
279,
16826);
|
Note
Comparing with Exercise 8:
The total number of records are identical
The node sequence is identical
The edge sequence is identical
The cost and agg_cost results are directly proportional
6.2. Cost Manipulations¶
When dealing with data, being aware of what kind of data is being used can improve results.
Vehicles can not circulate on pedestrian ways
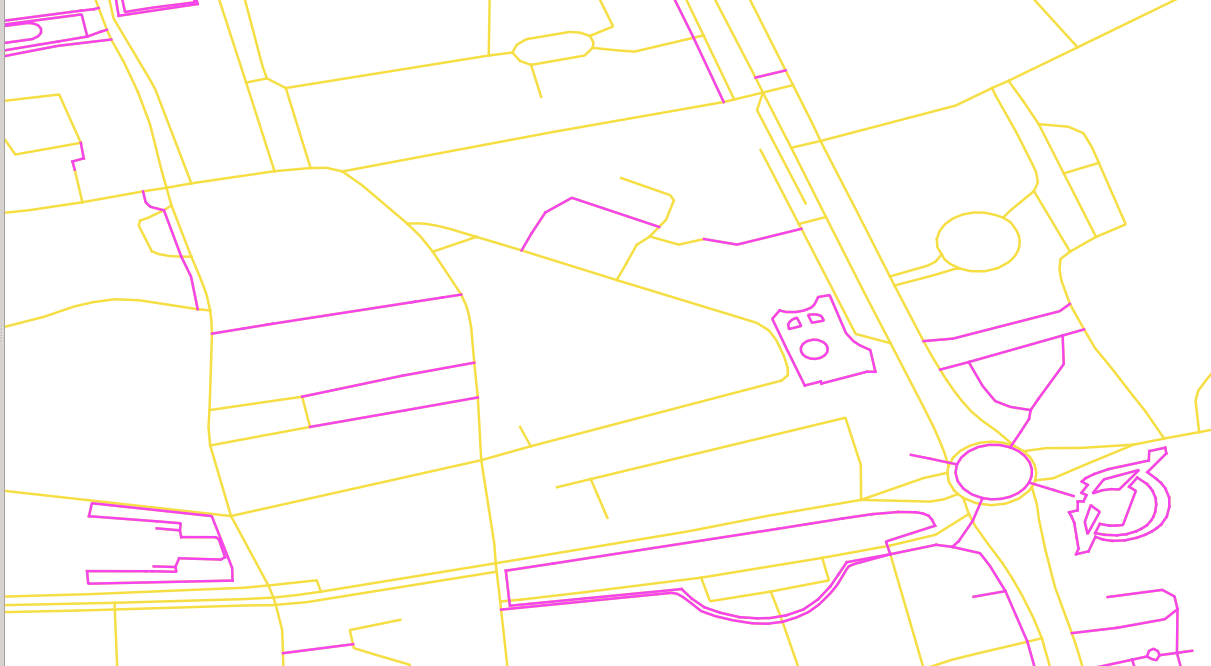
Penalizing or removal of pedestrian ways will make the results closer to reality.
When converting data from OSM format using the osm2pgrouting tool, there is an
additional table: configuration
The configuration table structure can be obtained with the following command.
city_routing=# \dS+ configuration
This is part of the results.
Table public.configuration
Column | Type | Nullable | Default | Storage |
------------------+------------------+-----------+---------+----------+
id | integer | not null | nextval | plain |
tag_id | integer | | | plain |
tag_key | text | | | extended |
tag_value | text | | | extended |
priority | double precision | | | plain |
maxspeed | double precision | | | plain |
maxspeed_forward | double precision | | | plain |
maxspeed_backward | double precision | | | plain |
force | character(1) | | | extended |
Indexes:
configuration_pkey PRIMARY KEY, btree (id)
configuration_tag_id_key UNIQUE CONSTRAINT, btree (tag_id)
Referenced by:
TABLE ways CONSTRAINT ways_tag_id_fkey FOREIGN KEY (tag_id) REFERENCES configuration(tag_id)
Options: autovacuum_enabled=false
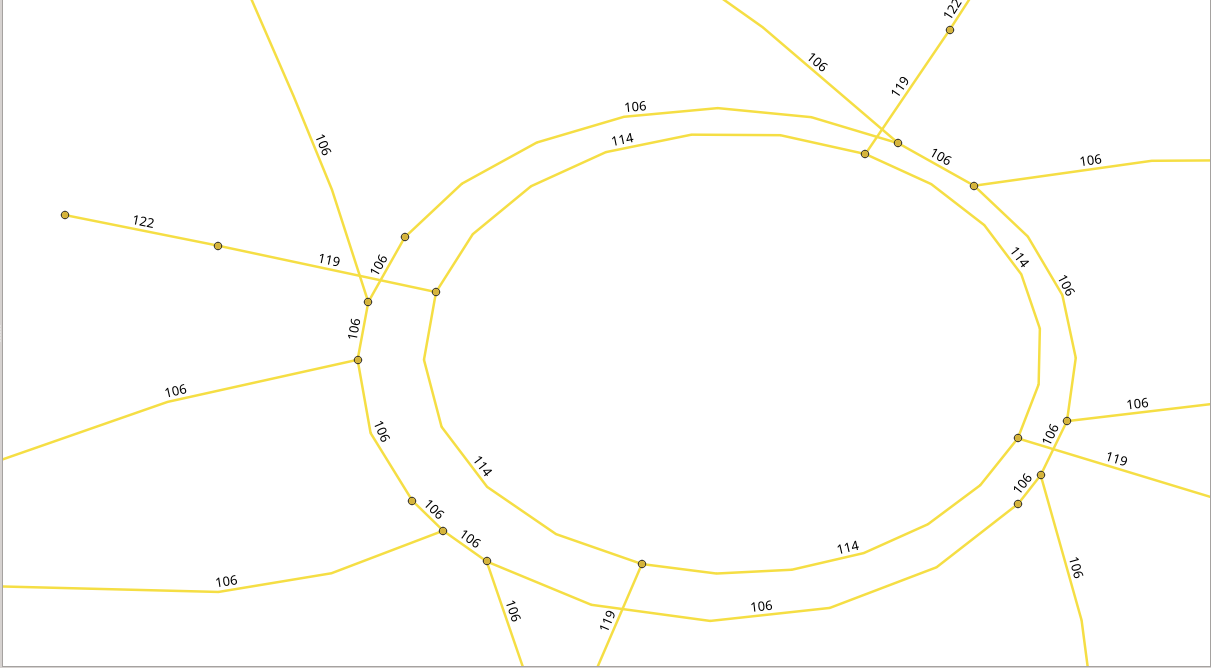
In the image above there is a detail of the tag_id of the roads.
OSM way types
SELECT tag_id, tag_key, tag_value FROM configuration ORDER BY tag_id;
tag_id | tag_key | tag_value
--------+-----------+-------------------
100 | highway | road
101 | highway | motorway
102 | highway | motorway_link
103 | highway | motorway_junction
104 | highway | trunk
105 | highway | trunk_link
106 | highway | primary
107 | highway | primary_link
108 | highway | secondary
109 | highway | tertiary
110 | highway | residential
111 | highway | living_street
112 | highway | service
113 | highway | track
114 | highway | pedestrian
115 | highway | services
116 | highway | bus_guideway
117 | highway | path
118 | highway | cycleway
119 | highway | footway
120 | highway | bridleway
121 | highway | byway
122 | highway | steps
123 | highway | unclassified
124 | highway | secondary_link
125 | highway | tertiary_link
201 | cycleway | lane
202 | cycleway | track
203 | cycleway | opposite_lane
204 | cycleway | opposite
301 | tracktype | grade1
302 | tracktype | grade2
303 | tracktype | grade3
304 | tracktype | grade4
305 | tracktype | grade5
401 | junction | roundabout
(36 rows)
Also, on the ways table there is a column that can be used to JOIN with the configuration table.
The ways types
SELECT distinct tag_id, tag_key, tag_value
FROM ways JOIN configuration USING (tag_id)
ORDER BY tag_id;
tag_id | tag_key | tag_value
--------+----------+----------------
106 | highway | primary
107 | highway | primary_link
108 | highway | secondary
109 | highway | tertiary
110 | highway | residential
111 | highway | living_street
112 | highway | service
113 | highway | track
114 | highway | pedestrian
117 | highway | path
118 | highway | cycleway
119 | highway | footway
122 | highway | steps
123 | highway | unclassified
124 | highway | secondary_link
125 | highway | tertiary_link
201 | cycleway | lane
202 | cycleway | track
204 | cycleway | opposite
(19 rows)
In this workshop, costs are going to be manipulated using the configuration table.
6.2.1. Exercise 10 - Vehicle routing without penalization¶
From the venue at National Theater Bucharest to Hotel Capitol

The vehicle is going from vertex
16826to vertex279.The vehicle’s cost in this case will be in seconds.
All roads have a
penaltyof1.Costs (in seconds) are to be multiplied by
penalty.Costs wont change (times 1 leaves the value unchanged).
The
configurationtable is linked with thewaystable by thetag_idfield using aJOIN.
ALTER TABLE configuration ADD COLUMN penalty FLOAT;
-- No penalty
UPDATE configuration SET penalty=1;
SELECT *
FROM pgr_dijkstra(
'
SELECT gid AS id,
source,
target,
cost_s * penalty AS cost,
reverse_cost_s * penalty AS reverse_cost
FROM ways JOIN configuration
USING (tag_id)
',
16826,
279);
6.2.2. Exercise 11 - Vehicle routing with penalization¶
Change the cost values for the configuration table, in such a way, that the
Pedestrian roads are not used.
Using residential roads is not encouraged.
Using “faster” roads is highly encouraged.
The
penaltyvalues can be changed withUPDATEqueries.
Note
These values are an exaggeration.
-- Not including pedestrian ways
UPDATE configuration SET penalty=-1.0 WHERE tag_value IN ('steps','footway','pedestrian');
-- Penalizing with 5 times the costs
UPDATE configuration SET penalty=5 WHERE tag_value IN ('residential');
-- Encuraging the use of "fast" roads
UPDATE configuration SET penalty=0.5 WHERE tag_value IN ('tertiary');
UPDATE configuration SET penalty=0.3 WHERE tag_value
IN ('primary','primary_link',
'trunk','trunk_link',
'motorway','motorway_junction','motorway_link',
'secondary');
From the venue at National Theater Bucharest to Hotel Capitol with penalization.
The vehicle is going from vertex
16826to vertex279.Use
cost_sandreverse_cost_scolumns, which are in unitseconds.Costs are to be multiplied by
penalty.The
configurationtable is linked with thewaystable by thetag_idfield using aJOIN.
SELECT * FROM pgr_dijkstra(
'
SELECT gid AS id,
source,
target,
cost_s * penalty AS cost,
reverse_cost_s * penalty AS reverse_cost
FROM ways JOIN configuration
USING (tag_id)
',
16826,
279);
Note
Comparing with Exercise 9:
The total number of records changed.
The node sequence changed.
The edge sequence changed.
The route is avoiding the residential roads that have
tag_id = 110.
